Rate of a reaction
The rate of reaction refers to the speed at which the products are formed from the reactants in a chemical reaction. It gives some insight into the time frame under which a reaction can be completed. For example, the reaction rate of the combustion of cellulose in fire is very high and the reaction is completed in less than a second.
What is Reaction Rate?
The rate of reaction or reaction rate is the speed at which reactants are converted into products. When we talk about chemical reactions, it is a given fact that rate at which they occur varies by a great deal. Some chemical reactions are nearly instantaneous, while others usually take some time to reach the final equilibrium.
This article aims to help students learn about and understand what exactly is the rate of reaction for a given chemical compound.
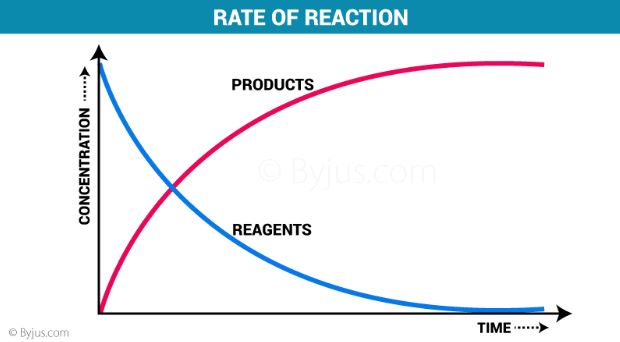
Factors affecting the rate of reaction
The various factions that can affect the rate of a chemical reaction are listed in this subsection.
Effect of concentration on reaction rate
- According to the collision theory, the rate of reaction increases with the increase in the concentration of the reactants.
- As per the law of mass action, the chemical reaction rate is directly proportional to the concentration of reactants.
- This implies that the chemical reaction rate increases with the increase in concentration and decreases with the decrease in the concentration of reactants.
- Time plays a major role in changing the concentration of reactants and products. Therefore, even time is a vital factor affecting the reaction rate.
Recommended Videos
Pressure factor
- Pressure increases the concentration of gases which in turn results in the increase of the rate of reaction. The reaction rate increases in the direction of less gaseous molecules and decreases in the reverse direction.
- Thus, it can be understood that pressure and concentration are interlinked and that they both affect the rate of reaction.
How does temperature affect the reaction rate?
- According to collision theory, a chemical reaction that takes place at a higher temperature generates more energy than a reaction at a lower temperature.
- This is because colliding particles will have the required activation energy at high temperature and more successful collisions will take place.
- There are some reactions that are independent of temperature. Reactions without an activation barrier are examples of chemical reactions that are independent of temperature.
Presence of Catalyst
- A catalyst can be defined as a substance that increases the rate of the reaction without actually participating in the reaction. The definition itself describes its effect on chemical reactions.
- The presence of a catalyst increases the speed of reaction in both forward and reverse reaction by providing an alternate pathway which has lower activation energy.
Surface Area of the Reactants
The surface area of reactants affects the rate of reaction. If the size of a particle is small, the surface area will be more and this increases the speed of heterogeneous chemical reactions.
More references
https://byjus.com/chemistry/rate-of-reaction/




No comments:
Post a Comment